Awesome Tips About Prepaid Expenses On The Balance Sheet
A “prepaid asset” is the result of a prepaid expense being recorded on the balance sheet.
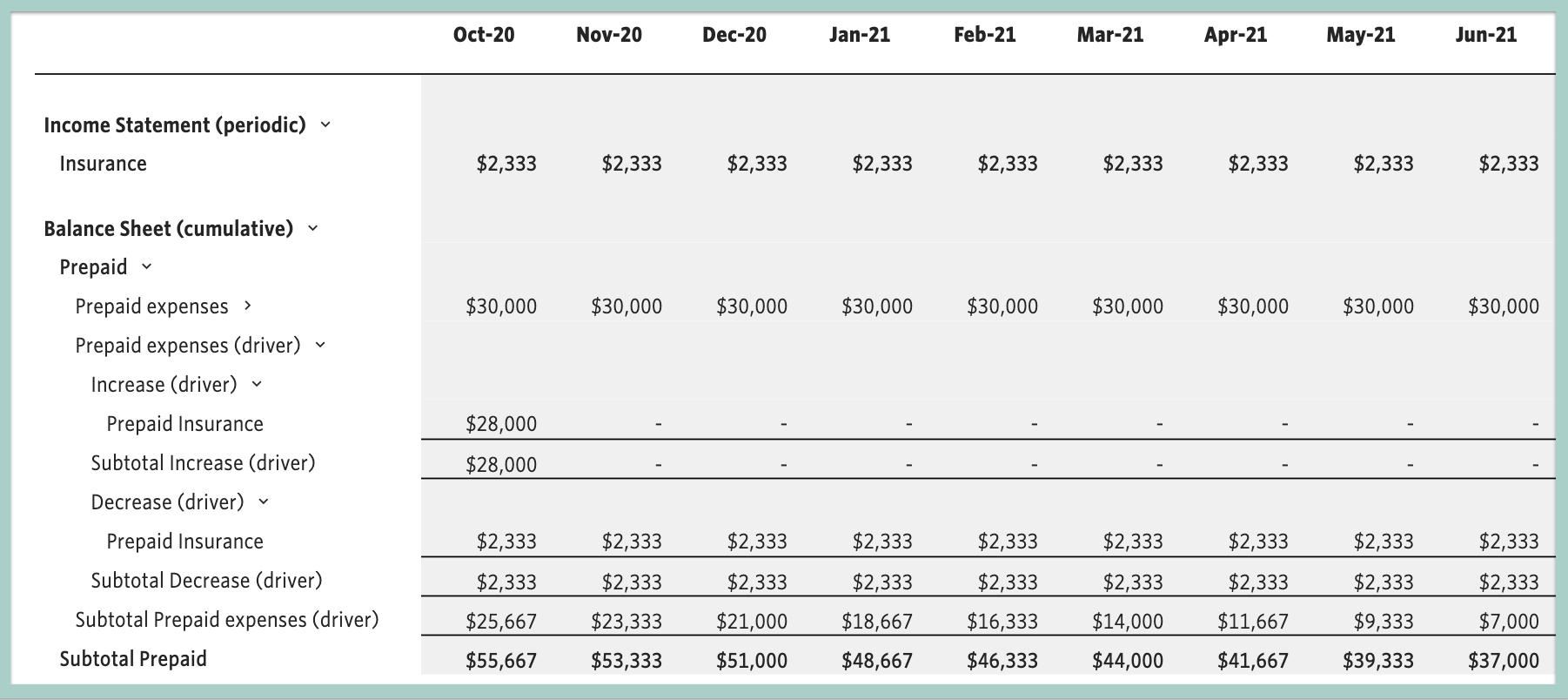
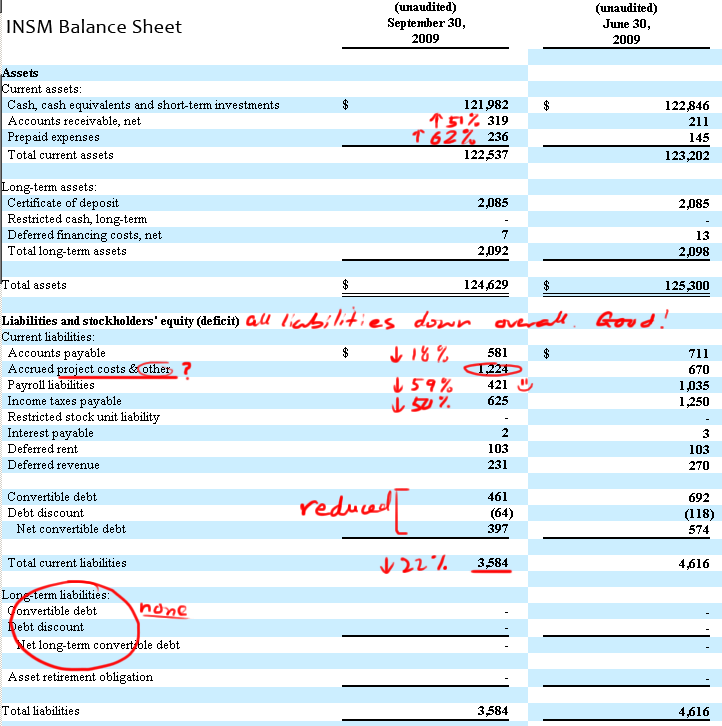
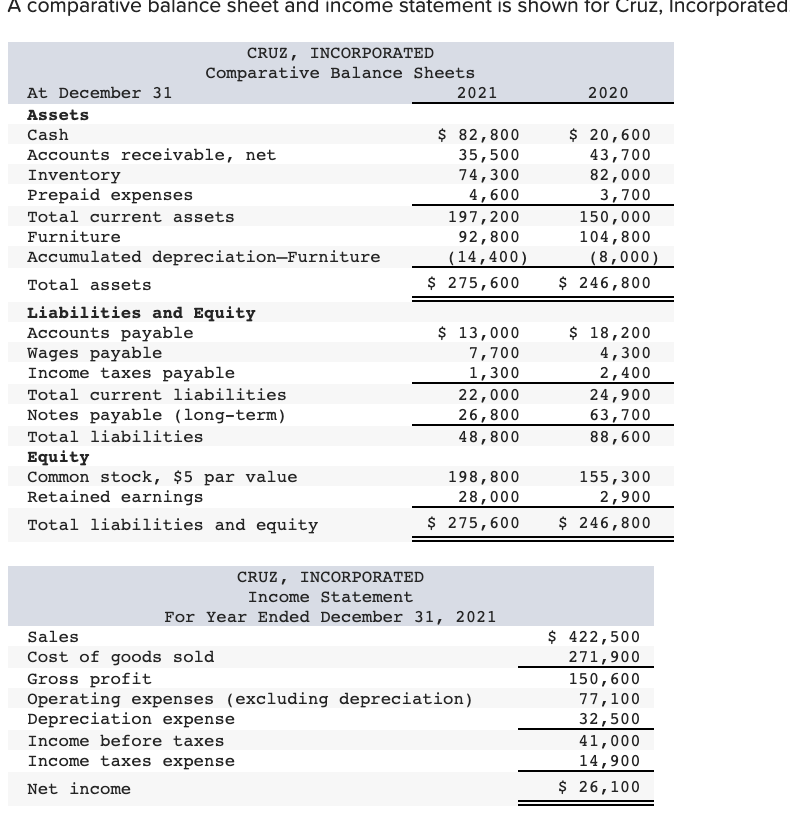
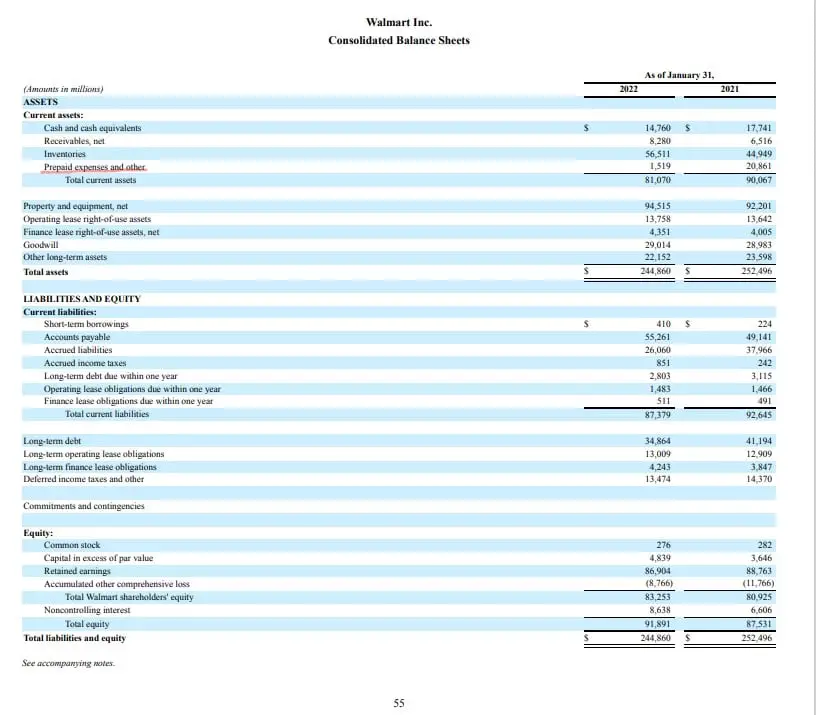
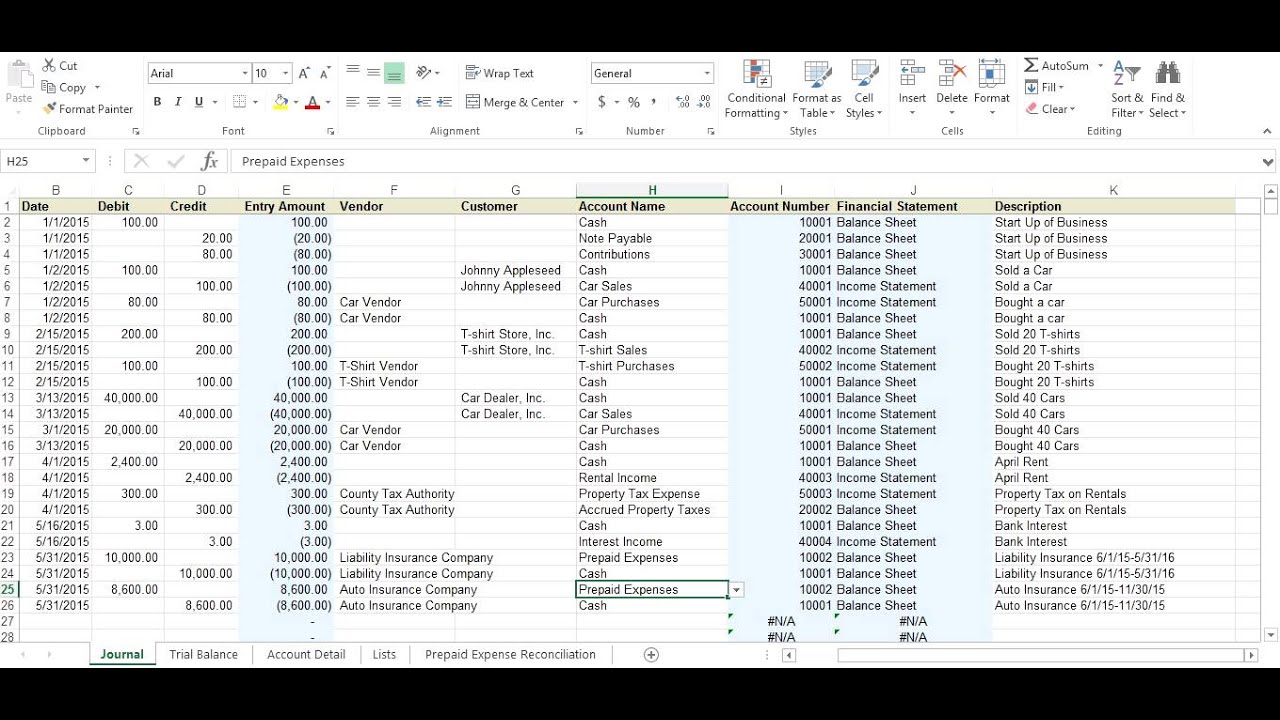
Prepaid expenses on the balance sheet. Prepaid rent will increase, while cash will decrease. Key takeaways a prepaid expense is an amount paid in advance for the goods or benefits that are to be received in the upcoming period. Prepaid expenses, or prepaid assets as they are commonly referred to in general accounting, are recognized on the balance sheet as an asset.
They are considered assets because the firm has paid for a future benefit in which the benefit has not yet been. Prepaid expenses refer to expenses that a company pays in advance for goods or services that it will receive in the future. The various prepayment expenses disbursed by a firm include paid off rent, insurance, interest, salary, utility bills,.
Effect of prepaid expenses on financial statements. Prepaid expenses (an asset account on the balance sheet). When a business pays in advance for products or services that will be received in the future, the prepaid expenses are recorded as assets on the balance sheet.
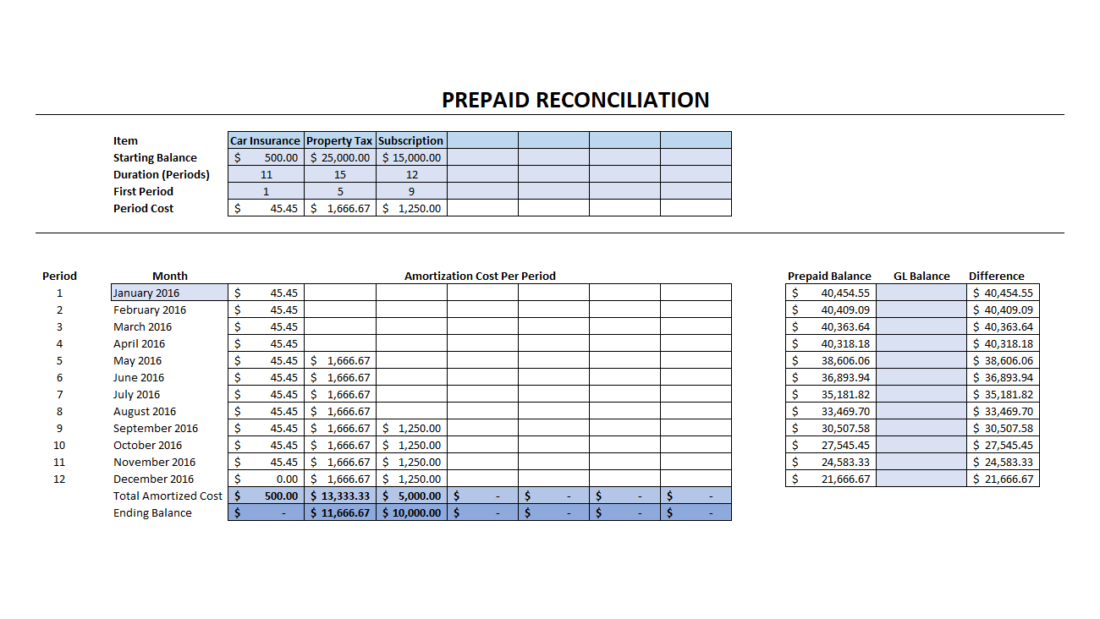
Their primary purpose is to allocate costs accurately between accounting periods and ensure that expenses are recognized in the period they contribute to generating revenue. The adjusting entry on january 31 would result in an expense of $10,000 (rent expense) and a decrease in assets of $10,000 (prepaid rent). Prepaid expenses, or prepaid assets as they are commonly referred to in general accounting, are recognized on the balance sheet as an asset.
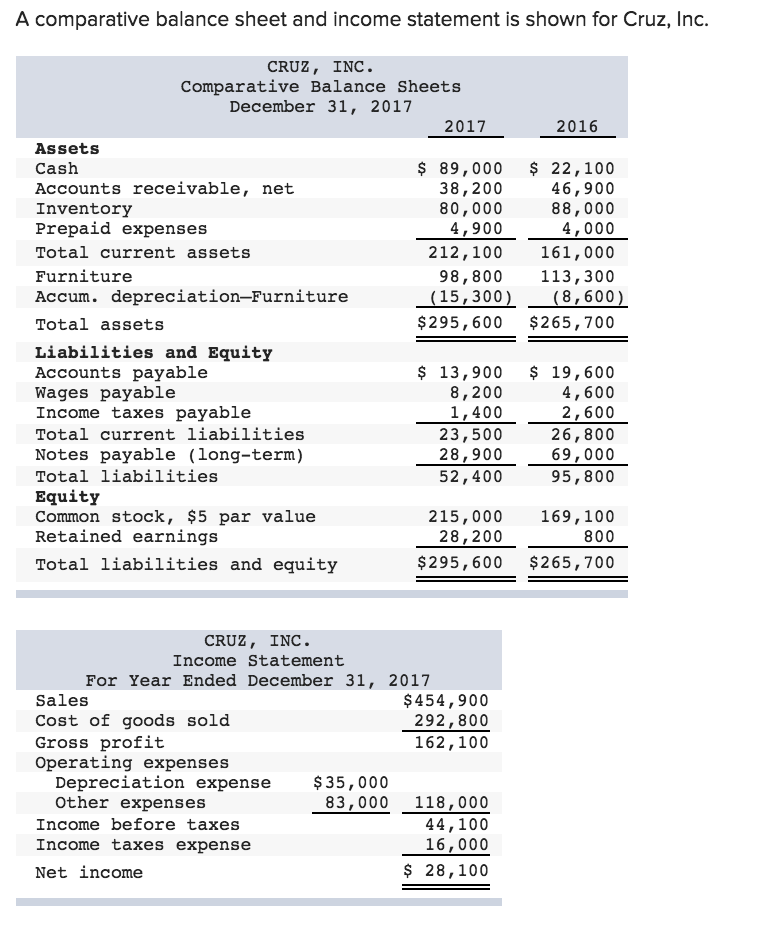
Therefore, there will be no changes in the totals for current assets or total assets. These expenses are considered assets on the company's balance sheet, as they represent an amount that the company has already paid, but for which it has not yet received the corresponding benefit. Prepaid expenses are originally listed as assets, but as time passes, their.
Prepaid expenses are treated as assets on a company’s balance sheet, as they represent future economic benefits. As an example, the whole purpose of. Prepaid expenses are basically future expenses which have been paid in advance, with common examples being insurance or rent.
Examples of prepaid expenses include insurance premiums, rent, or subscription services. A prepaid expense is an expense that has been paid in advance but from which no gain has yet been realized. Essentially, a business pays upfront for a good or service, and the benefit is received over time.
Prepaid expenses recorded as current assets because the company is legally entitled to receive the future benefits for which it. This means it will appear as one of your company's assets and increase its total value. These payments are recorded as assets on the balance sheet until they are used or consumed, at which point they become expenses on.
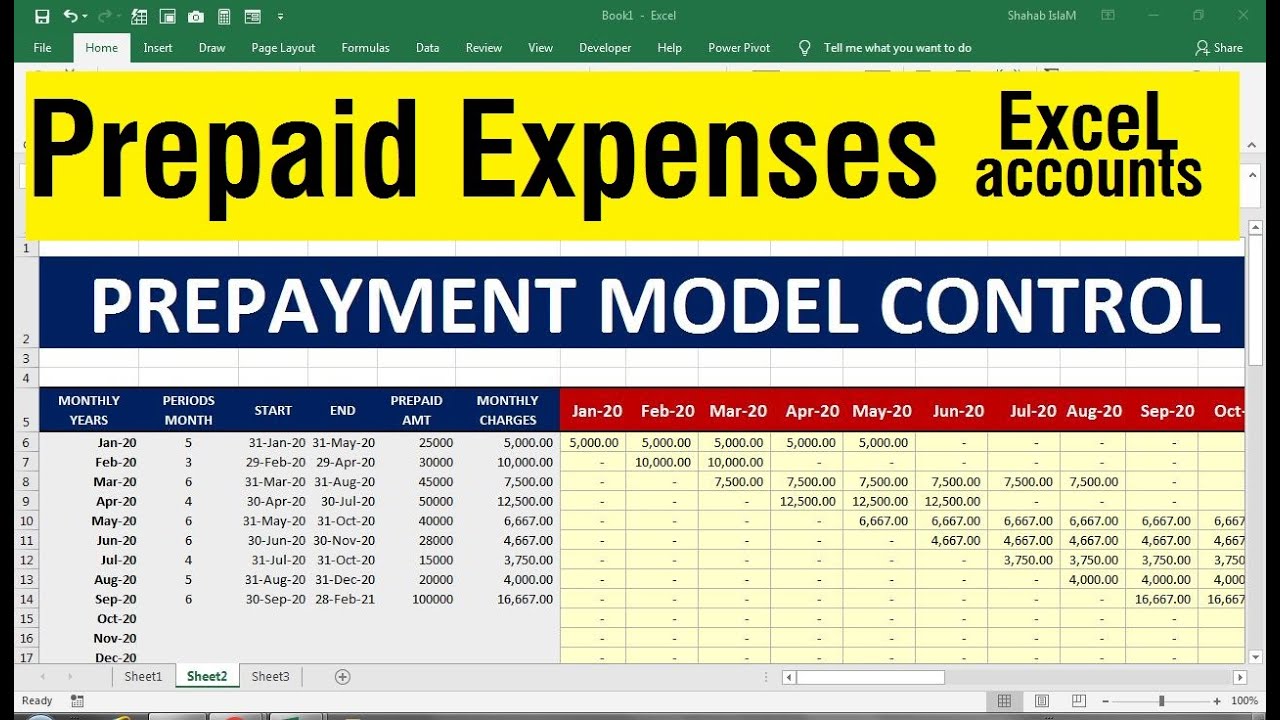
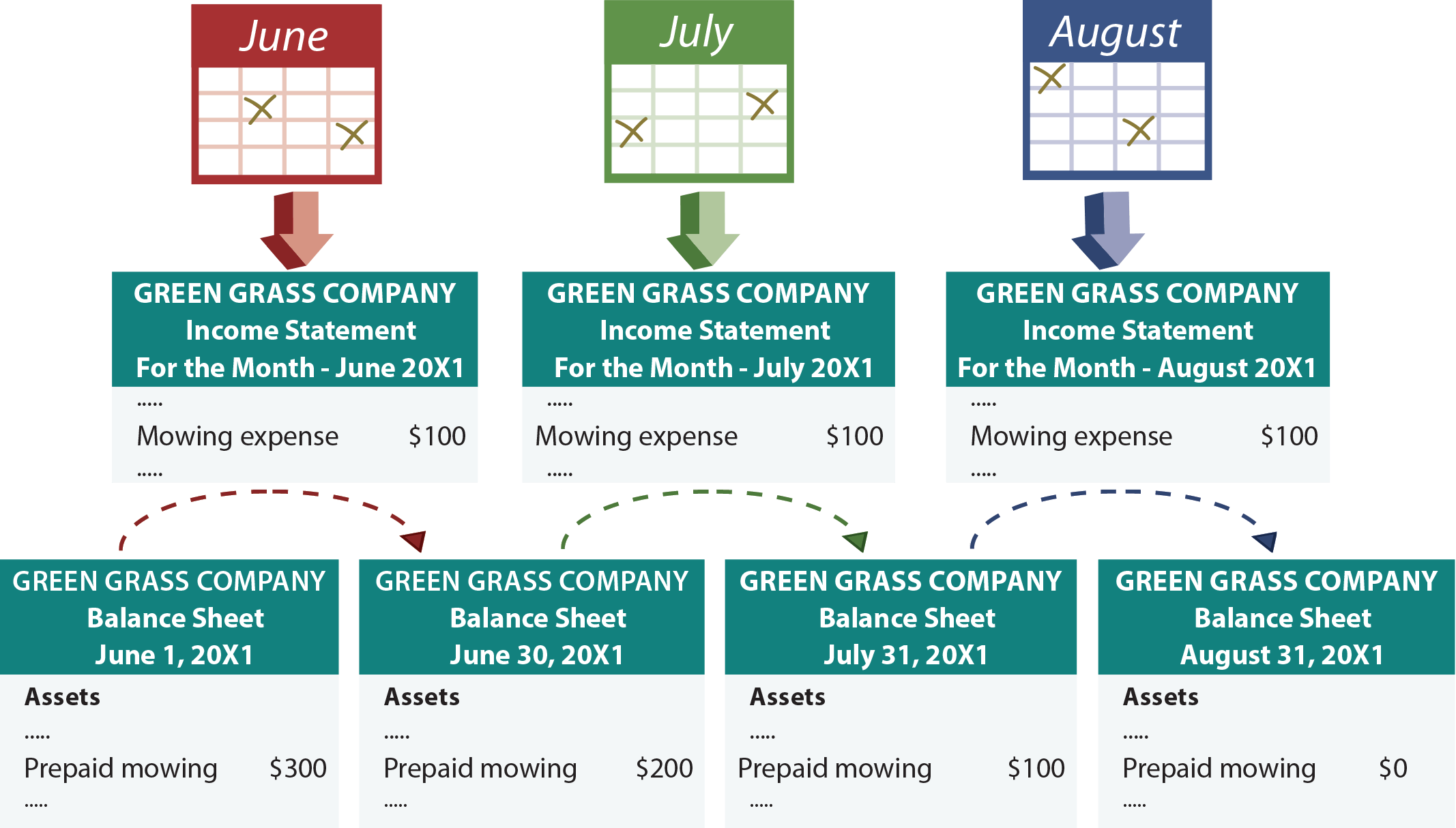
Prepaid expenses refer to payments made in advance for goods or services that a company will receive or use in the future. The gaap matching principle prevents expenses from being recorded on the income statement before. The adjusting journal entry for a prepaid expense, however, does affect both a company’s income statement and balance sheet.
Cash or bank (decreasing the cash or bank account) this entry reflects the payment made for the prepaid expense and recognizes it as an asset on the balance sheet because the company has paid for a future benefit. When you pay for a prepaid expense, the cost is recorded as an asset on your balance sheet. These expenses are initially documented as an asset on the firm’s balance sheet, and as its benefits are eventually realised over time, they would then be classified as an expense.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/prepaid-expense-4191042-recirc-blue-1d8d154bf0c94ba6858fe12907d2b694.jpg)