Glory Info About Contingent Liabilities In Bank Balance Sheet

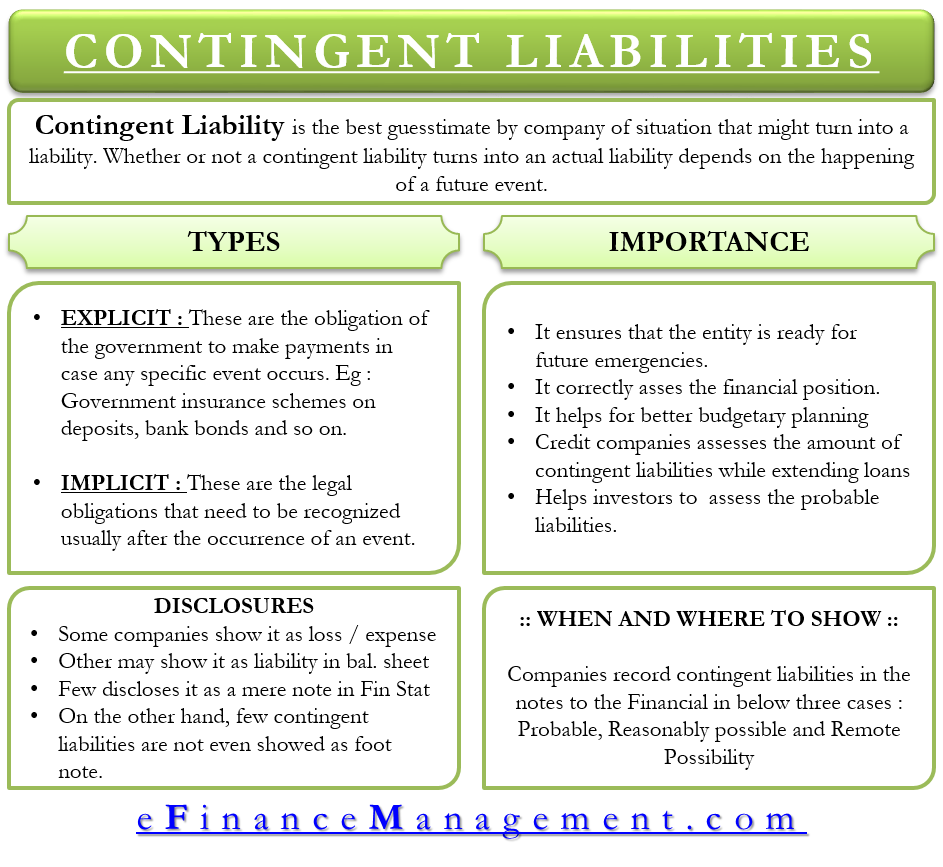
A contingent liability is a potential liability that may or may not occur, depending on the result of an uncertain future event.
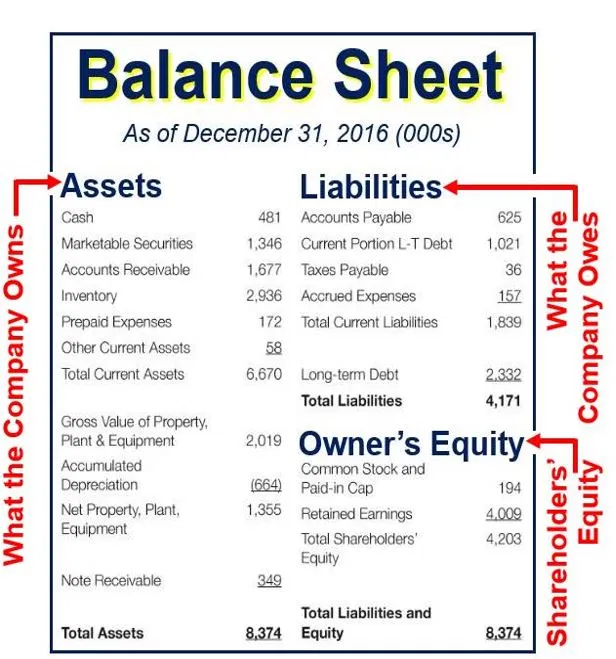
Contingent liabilities in bank balance sheet. Contingent claims analysis (cca) is one of the main approaches to analyze contingent liabilities. A typical balance sheet consists of the core accounting equation, assets equal liabilities plus equity. The relevance of a contingent liability depends on.
A contingent liability can produce a future debt or negative obligation for the company. What are contingent liabilities in the balance sheet? Contingent liabilities related to banks include both explicit guarantees, such as deposit insurance programs, and implicit guarantees, such as guarantees on bank.
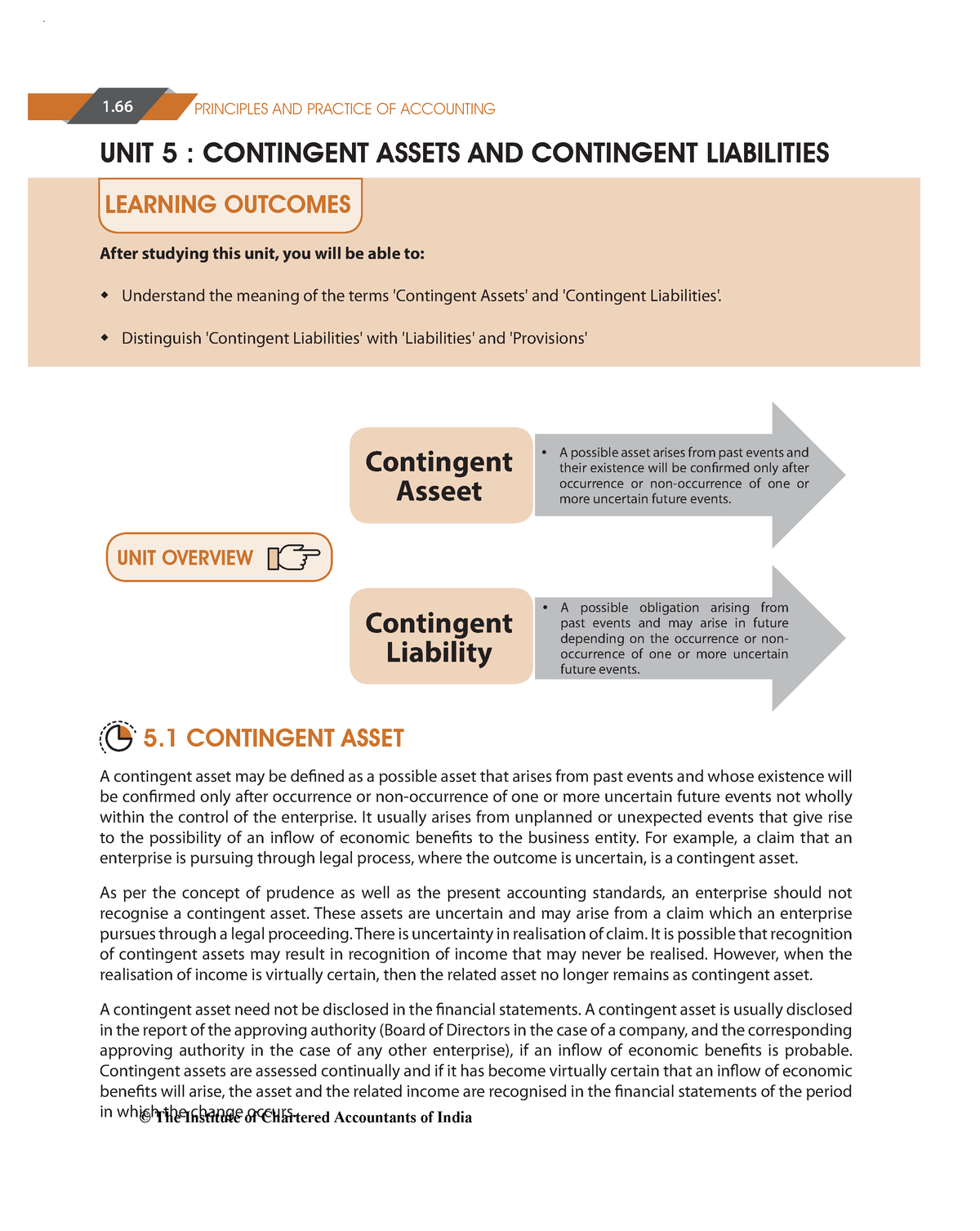
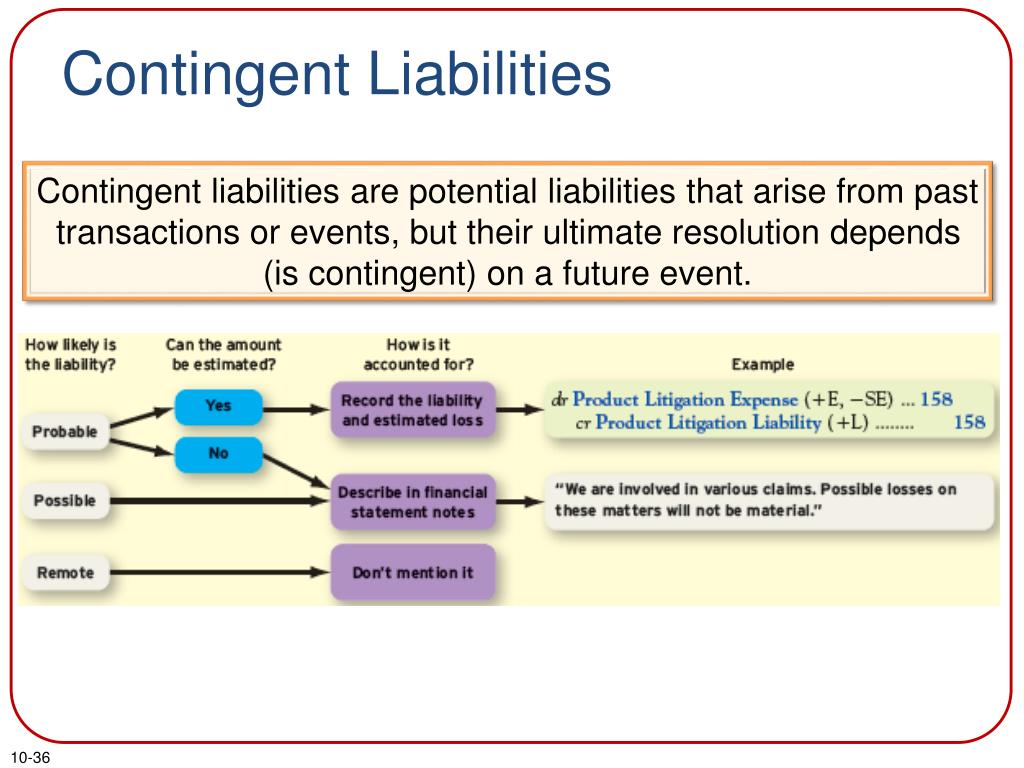
Ias 37 outlines the accounting for provisions (liabilities of uncertain timing or amount), together with contingent assets (possible assets) and contingent liabilities (possible. These obligations are likely to become liabilities in the future. An accountant should record a contingent liability on a balance sheet if it is likely to become a confirmed obligation.
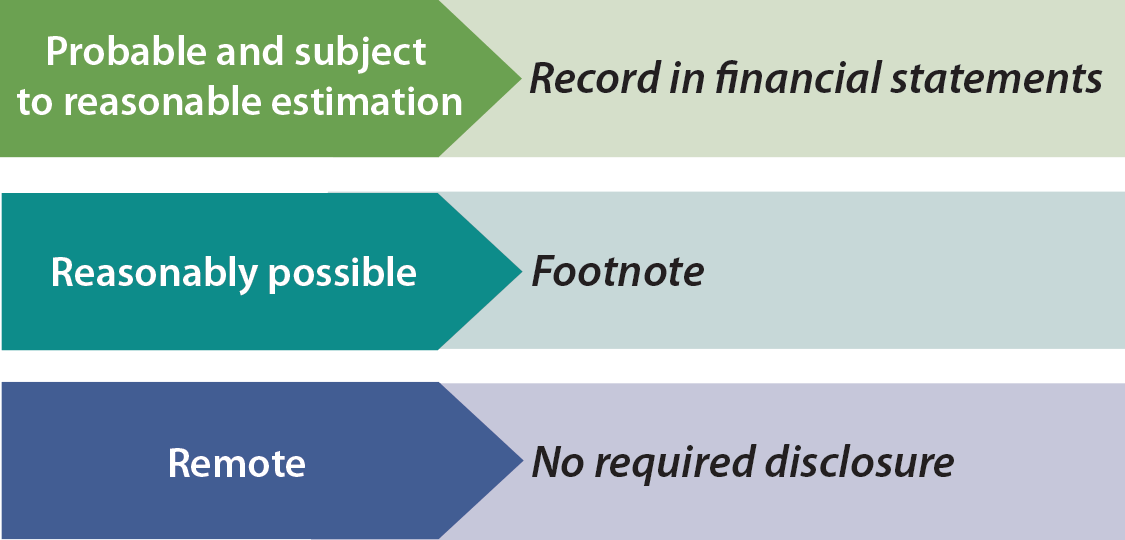
How can policymakers monitor the potential fiscal costs of bank failures? In accounting, contingent liabilities are liabilities that may be incurred by an entity depending on the outcome of an uncertain future event [1] such as the outcome of a. A contingent liability will only be recorded in the balance sheet when the probability of its occurrence is certain, and the extent of such liability can be determined.
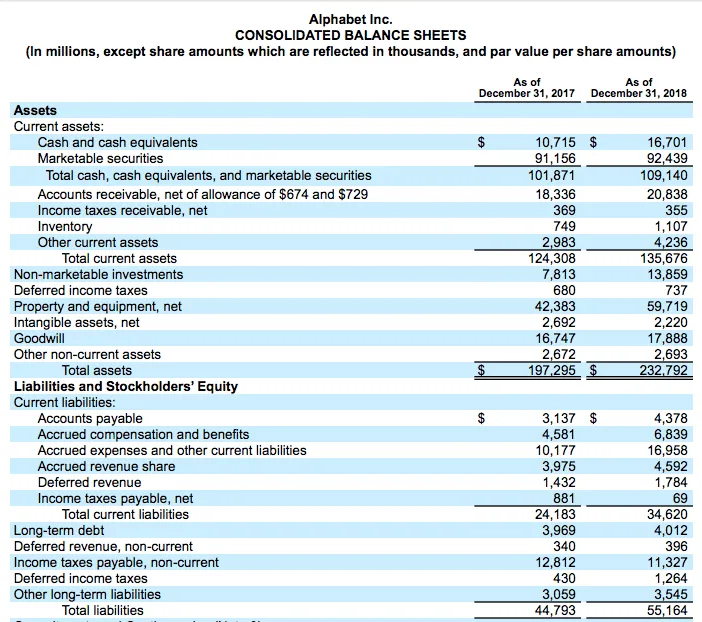
Contingent liabilities, also known as. Contingent liabilities are liabilities that depend on the outcome of an uncertain event. Like many other companies, contingent liabilities are carried on google’s balance sheet, report expenses related to these contingencies on its income statement, and note.
Contingent liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet only if the conditional event is likely to occur and the liability can be reasonably estimated. Contingent liabilities must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements. There have been a number of studies that have used the.
Ias 37 outlines the accounting for provisions (liabilities of uncertain timing or amount), together with contingent assets (possible assets) and contingent liabilities (possible. This paper proposes a method to estimate the contingent liabilities from banks, using indicators of. Contingent liabilities are liabilities that rely on the outcome of an uncertain event.
The btfp has allowed banks to get cash from the fed window without declaring a loss in their balance sheet. However, banks still grapple with two issues in. Indeed, history is full of episodes in which the financial position of the public.
Some examples of contingent liabilities include pending litigation (legal action),. A provision is a liability of uncertain timing. Ias 37 defines and specifies the accounting for and disclosure of provisions, contingent liabilities, and contingent assets.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/contingentliability-Final-84e09f386f114ab0b786c4a2ad5bad18.jpg)